Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) makes up over 80–90% of total RNA in most eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, significantly masking the detection of messenger RNA (mRNA) and non-coding RNAs in RNA sequencing. Efficient removal of rRNA is essential to improve the sensitivity and accuracy of transcriptome profiling, particularly in RNA-Seq and long-read sequencing technologies. This guide provides a detailed workflow for using the Ribo-off™ rRNA Depletion Kit V2, focusing on human, mouse, rat, and bacterial RNA samples.
Why rRNA Depletion Matters
In total RNA samples, the high abundance of rRNA obscures the sequencing depth for coding and non-coding RNAs. Removing rRNA increases the number of informative reads and enables better discovery of:
-
lncRNA ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
circRNA nih.gov
-
mRNA isoforms ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
bacterial transcripts ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
rRNA depletion is preferred over poly(A) enrichment when working with:
-
degraded samples ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
non-polyadenylated RNA nih.gov
-
microbial and dual RNA samples ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
About the Ribo-off™ rRNA Depletion Kit V2
The Ribo-off™ Kit V2 is a robust solution for depleting cytoplasmic and mitochondrial rRNA. It uses probe-based hybridization followed by RNase H digestion to selectively remove rRNA, preserving mRNA and other RNAs for downstream analysis.
Key Features:
-
Targets both 28S, 18S, 5.8S, and 5S rRNAs.
-
Compatible with fragmented or intact RNA.
-
Suitable for RNA inputs as low as 10 ng ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Workflow Overview
1. Total RNA Preparation
Extract total RNA using phenol-chloroform or column-based methods. Ensure integrity with an RNA Integrity Number (RIN) >7 using a Bioanalyzer or TapeStation ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
For reference protocols:
2. Hybridization with rRNA Probes
Incubate the RNA sample with a cocktail of DNA probes complementary to rRNA sequences. This forms RNA-DNA hybrids for enzymatic degradation.
Refer to probe specificity:
3. RNase H Digestion
Add RNase H to selectively cleave the RNA strand of RNA-DNA hybrids. This step ensures degradation of rRNA without affecting other RNA types.
More on RNase H:
4. DNase I Treatment
DNase I removes residual DNA probes to prevent downstream inhibition.
Learn about DNase protocols:
5. RNA Purification
Use magnetic beads or column-based cleanup to recover high-quality rRNA-depleted RNA.
Cleaning protocols:
Quality Control
After depletion, verify rRNA removal with:
-
Bioanalyzer electropherogram
-
Qubit RNA HS assay
-
qPCR for rRNA targets
QC guidelines:
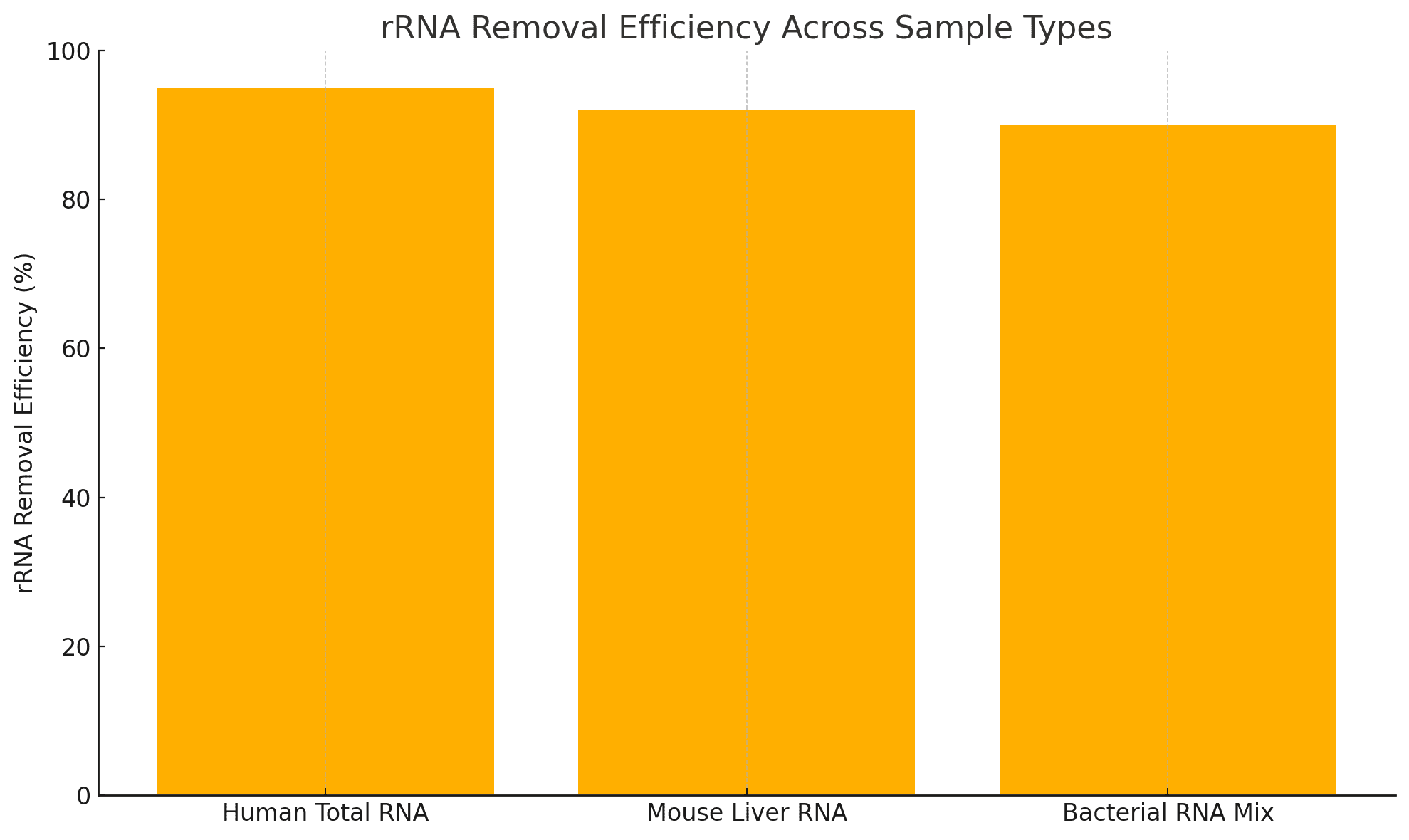
Example Performance
| Sample Type | rRNA Removal Efficiency | Input (ng) | Final Yield (ng) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human Total RNA | >95% | 100 | 40–60 |
| Mouse Liver RNA | >92% | 500 | 280–320 |
| Bacterial RNA Mix | >90% | 200 | 100–140 |
More data sources:
Applications in RNA-Seq
a. Strand-Specific RNA-Seq
Use depleted RNA for dUTP-based directional libraries ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
b. Metatranscriptomics
rRNA depletion is essential for environmental and host-pathogen studies ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
c. Single-Cell Sequencing
Bulk rRNA depletion improves detection in pooled single-cell analyses ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low RNA recovery | Overdigestion or improper cleanup | Reduce RNase H time |
| Residual rRNA peaks in QC | Incomplete hybridization | Increase hybridization temp/time |
| Inhibition in library prep | Incomplete DNase digestion | Extend DNase I treatment |
See troubleshooting:
Conclusion
The Ribo-off™ rRNA Depletion Kit V2 offers a reliable and efficient workflow for depleting rRNA from various RNA sources. Its compatibility with both human and bacterial samples makes it highly versatile for complex transcriptomic studies. By following this detailed workflow, researchers can maximize the sensitivity and accuracy of RNA-based assays, particularly for non-coding RNA discovery and sequencing of rare transcripts.
For further protocols and official technical documentation, refer to: